Blog
Table of Contents
Most crypto miners budget for hardware and electricity—but that’s just the beginning. Cooling systems, repairs, idle time, and even your setup location can quietly eat away at your returns. Over time, these hidden costs add up, cutting deep into your profits if not managed properly.
Key Takeaways
Electricity and cooling costs form the largest hidden expenses in crypto mining. Efficient machines and smarter energy use are key to staying profitable.
Regular maintenance and minimizing downtime protect mining operations from costly losses. Scheduling upkeep and quick repairs keep rigs running efficiently and increase earnings.
Home mining has higher costs and challenges than industrial setups, but careful planning can keep it profitable.
Crypto Mining Costs Breakdown
Electricity Expenses
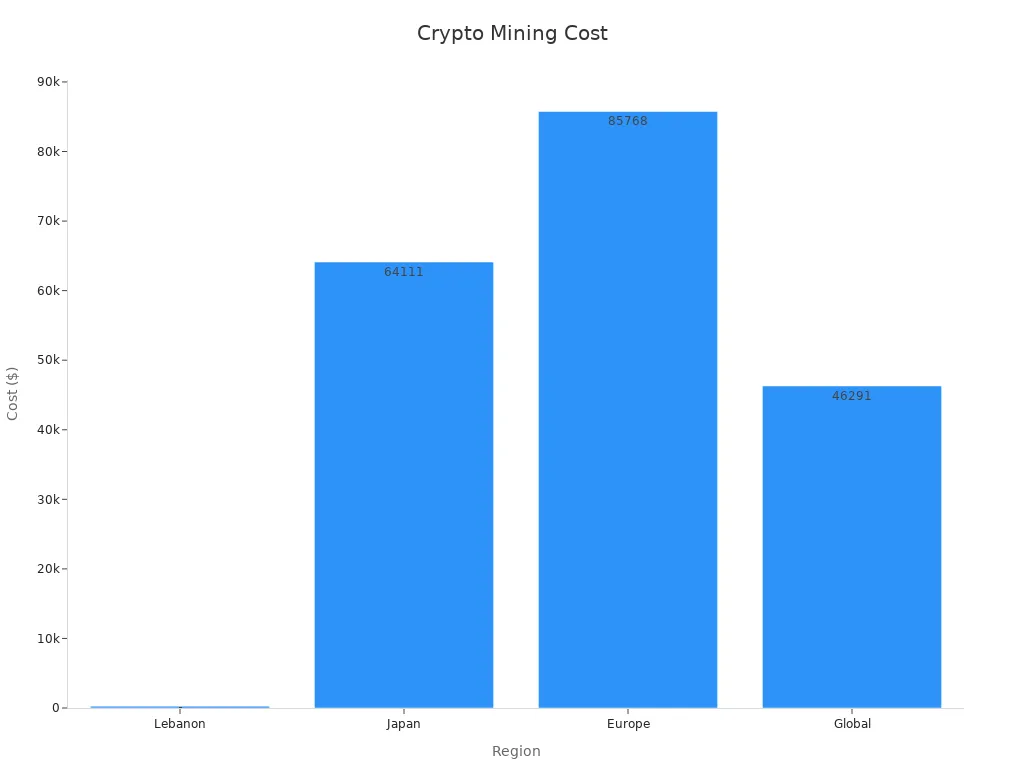
Electricity consumption stands as the largest driver of crypto mining costs. Home miners and industrial operations both face significant expenses, but the scale and efficiency differ. Home setups often use less efficient hardware, leading to higher electricity consumption per unit of cryptocurrency mined. Industrial miners deploy advanced machines, such as the MicroBT Whatsminer M63s hydro 390T, which consumes 7.215 kW and requires over 6.3 million kWh to mine a single Bitcoin. Regional electricity prices create wide disparities in expenses. For example, mining one Bitcoin in Lebanon costs about $266, while in Ireland, the same process can reach $321,112. The global average household electricity cost to mine one Bitcoin is $46,291, which exceeds the average Bitcoin price in July 2023.
Beyond basic electricity rates, power quality emerges as a critical—and often underestimated—hidden cost. Sensitive ASIC mining hardware faces severe threats from voltage fluctuations: sudden spikes or sags can inflict catastrophic damage. This includes fried motherboards, burned-out power supply units (PSUs), and even potential fire hazards.
Mitigating these risks demands significant investment in protective infrastructure:
Voltage stabilizers to regulate inconsistent supply.
Surge protectors to shield against transient spikes.
UPS systems to handle outages and ensure safe shutdowns.
The true cost lies beyond the initial purchase. Acquisition, installation, ongoing maintenance, and the inherent energy consumption of these protective systems layer on substantial, frequently overlooked hidden operational costs. These costs persistently erode mining margins, silently consuming potential profits.
Cooling Needs
Cooling represents another major component of crypto mining costs. Both home and industrial miners must manage heat generated by hardware. Home miners may use basic fans or air conditioning, which adds to electricity consumption and expenses. Industrial operations invest in advanced cooling systems, such as hydro or immersion cooling, to maintain optimal temperatures and reduce downtime. These systems increase upfront expenses but lower long-term costs by improving hardware efficiency and lifespan.
Future trends show rising electricity consumption due to higher hash rates and more powerful hardware. Regulatory changes, such as increased tariffs and mandatory energy surveys, will likely raise crypto mining costs.
Maintenance and Downtime
Regular Upkeep
Mining operations require constant attention to regular upkeep. These ongoing expenses often fall into the category of hidden costs that many miners underestimate. As the average cost to mine a single Bitcoin skyrocketed from $6,253 in 2020 to over $26,218 in 2024 – have you uncovered the hidden cost traps eating into your profits?
ASIC miners need regular maintenance like dust cleaning, thermal paste replacement, and fan checks. Neglect risks component failure (fans, chips, PSUs burning out), leading directly to downtime = lost rewards. Spare parts and labor costs add up, especially without DIY repair skills.
Use digital tools to track maintenance. By following manufacturer guidelines and adjusting schedules based on operational experience, mining operations can reduce repair costs and extend equipment life. Ongoing expenses for upkeep directly affect the bottom line, making them a critical part of mining operations.
Downtime Impact
Downtime represents one of the most damaging hidden costs in mining operations. When rigs go offline for maintenance, power outages, or unexpected failures, they stop generating revenue. The opportunity cost from halted mining activity often exceeds the direct costs of repairs or upkeep.
Prompt repairs and on-site technicians help minimize downtime, protecting profitability in mining operations.
Frequent downtime increases ongoing expenses and reduces the efficiency of operations. Mining operations that prioritize quick response and preventive maintenance can limit these losses. Effective management of downtime and regular upkeep ensures that mining operations remain competitive and profitable, even as costs and ongoing expenses continue to rise.
Hardware Depreciation
Equipment Value Loss
Crypto mining operations face significant costs from hardware depreciation. A top-tier ASIC miners today could become unprofitable tomorrow, due to:
Newer models with superior hash rates and energy efficiency, quickly outpacing older hardware.
Declining mining rewards over time.
Bear markets, which can abruptly erode resale value.
Mining equipment loses value quickly due to rapid technological advances and constant use. The Galaxy Digital report shows that most miners use a median useful life of three years to calculate depreciation. This approach helps normalize costs and provides a clear picture of equipment value loss over time.
Upgrade Timing
Timing hardware upgrades plays a crucial role in controlling costs and maximizing returns. Miners must monitor several factors to decide when to replace old machines. The table below summarizes key considerations:
Factor | Description / Value Range |
|---|---|
Bitcoin Price Volatility | High fluctuations impacting mining profitability |
Mining Hardware Costs | Choose reliable suppliers to obtain competitive prices. |
Energy Consumption & Costs | Electricity rates $0.01-$0.075/kWh affect ROI |
Hardware Performance Metrics | Hash rates 200-335 TH/s; power use 12W/T-42W/T |
Daily Net Profit Examples | Losses up to -$38.1 to profits $47.22 |
Miners use profitability calculators and market analysis tools to track these factors. They also consider hash rate, energy efficiency, and uptime. By upgrading at the right time, miners reduce operational costs and stay competitive. Regular evaluation of mining equipment ensures that operations remain profitable as technology and market conditions change.
Network and Tools Costs
Internet and Connectivity
Stable, high-speed connection required – Avoids rejected shares and downtime.
Industrial-scale minin need dedicated/backup lines.
VPNs, remote tools, & dedicated IPs add recurring expenses.
Location impacts cost – Remote areas face higher fees.
Tip: Mining operations should monitor network performance to catch issues early and avoid unexpected costs.
Management Software
Effective software tools help miners optimize performance, reduce downtime, and manage costs. From monitoring hardware health to automating tasks, the right software can significantly impact profitability. However, these solutions often come with subscription fees, setup complexity, or maintenance requirements—adding to operational expenses.
Free or Paid Tools like Braiins OS+ or Hiveon
Custom tools for performance monitoring & remote management
Noise and Safety
Noise Control
Cryptocurrency mining equipment generates significant noise, especially from high-speed fans and cooling systems. This issue is particularly sensitive in residential or urban environments, where many users are forced to invest in soundproof enclosures or modify garages and outdoor sheds to reduce noise disturbance.
Many miners tend to overlook these necessary indirect investments, but in reality, they are one of the many hidden costs of mining operations.
Beyond noise concerns, miners must also navigate increasingly strict regulatory requirements. In certain cities, setting up a mining operation may require permits, noise assessments, or even environmental impact studies. Depending on the location, some cities enforce noise regulations that miners may unknowingly violate.
Be aware that some cities have strict noise regulations, which miners may unknowingly violate if they don’t research local laws in advance.
In addition, mining site security should not be overlooked. To meet insurance and regulatory standards, many mining farms are required to install surveillance cameras, fire suppression systems, and even maintain 24/7 on-site security personnel to guard against equipment theft and potential fire hazards.
Scaling Costs
Infrastructure Upgrades
Crypto mining operations often face rising costs when scaling up. Infrastructure upgrades become necessary as the number of mining rigs grows. Operators may need to install new electrical panels, upgrade wiring, or add backup generators. These improvements help maintain operational efficiency and prevent power outages. Many operations also invest in advanced cooling systems to handle increased heat output. Upgrades like immersion cooling or hydro cooling can improve operational efficiency but add to initial and ongoing costs.
A table below shows common infrastructure upgrades and their impact on costs:
Upgrade Type | Purpose | Impact on Costs |
|---|---|---|
Electrical Upgrades | Support more rigs | High initial costs |
Cooling Systems | Manage heat | Ongoing costs |
Backup Generators | Prevent downtime | Maintenance costs |
Operators who plan upgrades carefully can control costs and boost operational efficiency. Delayed upgrades often lead to equipment failures and lost revenue.
Expanding Operational Space in Crypto Mining
As mining operations expand, the demand for larger operational space grows accordingly. More spacious facilities improve airflow, enhance cooling efficiency, and boost overall operational performance. However, renting or purchasing additional space significantly increases costs. Some miners opt to invest in building custom data centers, which offer high efficiency but require substantial upfront capital. Others prefer leasing warehouse space to reduce initial expenses.
Compared to large-scale operations, home crypto mining offers a more flexible and accessible option—especially for beginners or individuals with limited resources. While challenges such as higher residential electricity rates, limited access to 240V outlets, and the need for electrical upgrades do exist, a properly configured setup can still run efficiently and reliably.
By using soundproof enclosures, low-power ASIC devices, smart temperature-controlled fans, and optimized wiring, home users can effectively manage heat and noise while improving energy efficiency. Certain models like the Elphapex DG Home 1 or IceRiver AE0 are proven to run with minimal disruption in home environments, making them suitable for entry-level mining or small-scale testing setups.
Profit Strategies 2025
Efficient Hardware
Selecting advanced mining hardware stands as one of the most effective profitability strategies for 2025. Next-generation ASIC miners deliver higher hash rates and improved energy efficiency, which directly lowers electricity consumption and operational costs. Mining hardware now features smaller designs, enhanced cooling, and reduced power use. For example, next-gen ASICs can cut energy consumption per terahash nearly in half compared to older models, dropping the break-even Bitcoin price from $80,000 to $45,000 at the same electricity rate. Strategic location choices with cheap, abundant power further boost returns. Continuous upgrades remain essential, as hardware quickly becomes obsolete in this fast-moving industry.
Aspect | Older Hardware (30 W/TH) | Next-Gen ASIC (16.5 W/TH) |
|---|---|---|
Energy Consumption per TH | 30 W/TH | 16.5 W/TH |
~$80,000 | ~$45,000 |
Coin Selection
Choosing the right coin to mine is critical for maximizing profitability. Block rewards, network difficulty, hardware requirements, and electricity consumption all influence returns. ASICs are necessary for Bitcoin, Litecoin, and Dogecoin, while GPUs or CPUs work for coins like Monero and Ethereum Classic. Merged mining, such as combining Litecoin and Dogecoin, can increase earnings. Mining pools offer more consistent payouts. Miners should use calculators to compare daily returns and switch coins as market conditions change. Understanding local laws, energy prices, and hardware availability helps miners adapt their strategies for 2025 home mining and industrial operations.
FAQ
What is the most overlooked cost in crypto mining?
Many miners ignore cooling expenses. Cooling systems use extra electricity and require maintenance. These costs can reduce profits more than expected.
How does hardware depreciation affect mining profits?
Hardware loses value quickly. Newer models become available often. Miners must upgrade equipment to stay competitive, which increases overall costs.
Are home mining setups still viable given these hidden costs?
Yes, but only when using ultra-efficient miners (e.g., 2025’s latest low-power ASIC models) and securing the lowest possible electricity rates, as residential energy costs and hidden expenses typically reduce potential profits by 30-50%.
What’s the single most effective way to control hidden costs?
Preventive maintenance:scheduled cleaning, thermal management, and component replacements can reduce unexpected downtime by 60% and extend hardware lifespan by 6-12 months.



























 Bitdeer
Bitdeer Bitmain
Bitmain BOMBAX
BOMBAX DragonBall
DragonBall Elphapex
Elphapex Fluminer
Fluminer Goldshell
Goldshell iBelink
iBelink Iceriver
Iceriver Ipollo
Ipollo Jasminer
Jasminer Volcminer
Volcminer Aleo Miner
Aleo Miner