
Blog
SHA-256 is the main cryptographic hash function in bitcoin mining. This algorithm changes data into a code with a set length. It is almost impossible to undo this process or find two inputs with the same result. Bitcoin uses this to keep transactions safe and connect each block. Miners try to solve hard SHA-256 puzzles. They add new blocks and stop double-spending. In 2025, the global bitcoin network hashrate went over 1 ZettaHash per second. Special hardware like ASIC machines became very important for miners. This helps them keep up with harder mining and better network safety.
Key Takeaways
SHA-256 is a safe algorithm. It changes any data into a special 256-bit code. This helps keep Bitcoin transactions safe and honest.
Bitcoin miners use SHA-256 to solve puzzles. They change a number called a nonce. They keep trying until they find a code that matches the network’s difficulty level.
Mining hardware has changed over time. People first used CPUs, then GPUs, and now special ASIC machines. These new machines work much faster and use less energy for SHA-256.
ASIC miners are the best for Bitcoin mining. They are made only to run SHA-256. This gives miners more power and better chances to win rewards.
Bitcoin changes mining difficulty every two weeks. This keeps block times steady and protects the network from attacks. It helps keep Bitcoin safe for a long time.
SHA-256 Algorithm Basics
What Is SHA-256?
SHA-256 is a cryptographic hash function. It is the main algorithm in Bitcoin’s proof-of-work system. This algorithm takes any input and makes a 256-bit output. The size of the input does not matter. The output is called a hash. SHA-256 is part of the SHA-2 family. It is a standard approved by NIST. People use it for digital signatures, blockchain, and checking data integrity. The features of SHA-256 make it great for cryptocurrency mining, especially in Bitcoin. Some important properties of SHA-256 are:
Advantages & Key Properties of SHA-256:
Fixed-Length Output & Efficiency:
Generates a fixed 256-bit (32-byte) hash value for any input size.
Computationally efficient, producing hash values quickly for faster data processing.
Data Integrity & Avalanche Effect:
Ensures data remains unaltered during transmission or storage.
Any change to the input data, no matter how small, results in a drastically different hash value (avalanche effect).
Preimage Resistance (One-Way Function):
Computationally infeasible to reverse the hash function or calculate the original input data from its hash value (one-way function design).
Resistant to preimage attacks; attackers cannot feasibly guess the input.
Collision Resistance & Large Hash Space:
Extremely improbable for two different inputs to produce the same hash value (collision resistant).
While a mathematical possibility (theoretical collision risk), finding collisions is computationally infeasible due to the enormous hash space (2²⁵⁶ possible combinations).
This large hash space makes brute-force attacks impractical.
Drawback of SHA-256:
- Irreversibility: Data cannot be recovered or decoded from its hash value back to its original form (inherent to its one-way function design).
How SHA-256 Works
SHA-256 works in several steps. First, it pads the input so the length is a multiple of 512 bits. Then, it adds 64 bits to show the original message length. The algorithm splits the data into 512-bit blocks. Each block goes through 64 rounds of steps. These steps use bitwise shifts, modular addition, and mixing functions. This makes the output hash hard to guess and very secure.
Here is a simple overview of the process:
Pad the input and add the length.
Start with buffers set to certain constants.
Break the message into 512-bit pieces.
Process each piece through 64 rounds of mixing and compression.
Make the final 256-bit hash.
Note: The avalanche effect in SHA-256 means a tiny change in the input, like one letter, will make a totally different hash.
Why Bitcoin Uses SHA-256
Bitcoin uses SHA-256 as its proof-of-work algorithm. It gives both security and efficiency. Its collision resistance and one-way function keep the blockchain safe from fraud. SHA-256 also helps miners solve hard puzzles. This keeps the network secure.
Satoshi Nakamoto picked SHA-256 for Bitcoin after lots of cryptographic testing. The algorithm’s double hashing in Bitcoin (using SHA-256 two times) gives extra safety. SHA-256 also helps make safe Bitcoin addresses and checks transactions. Its strong security and reliability make it the main part of Bitcoin’s proof-of-work and cryptocurrency mining.
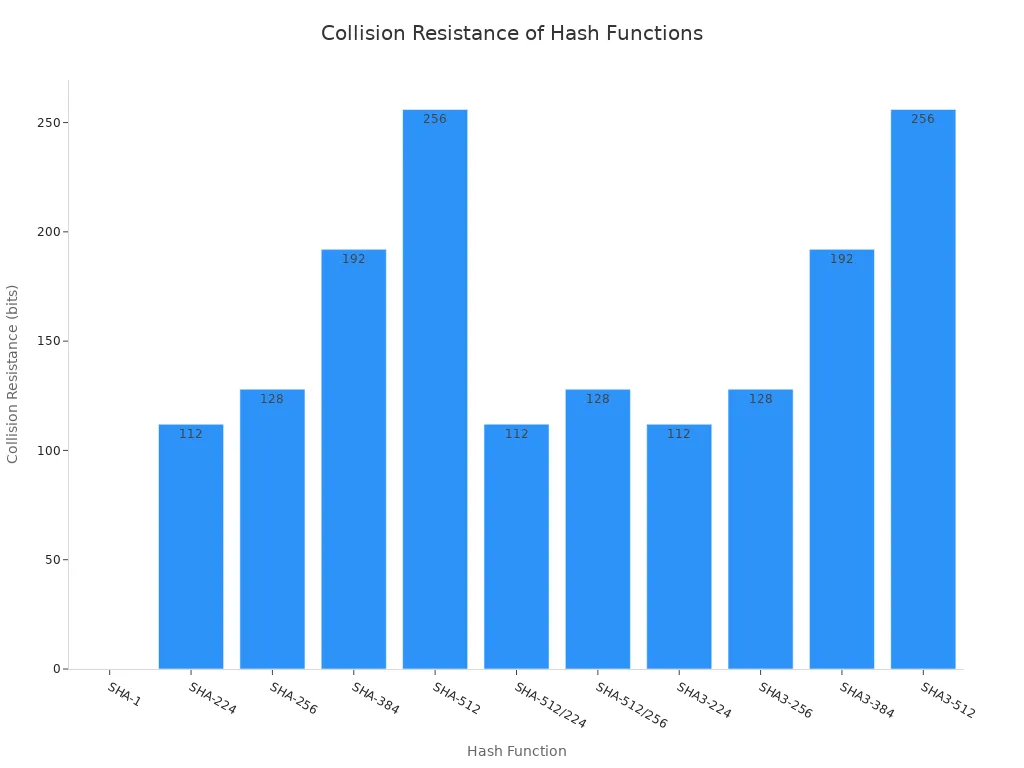
Other blockchains may use other algorithms. But SHA-256 is still a top choice for proof-of-work because it is safe and works well.
SHA-256 in Mining
Mining Process Overview
Bitcoin mining uses SHA-256 as its main tool. Miners start by picking transactions from the mempool. They like ones with higher fees because space is tight. Next, miners put these transactions into a new block. To keep the block safe, miners use SHA-256 to make a Merkle root. This root joins all the transaction hashes together. The miner then makes a block header. The block header has different fields. Each field helps with mining.
Bytes | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
4 | Version | Block version showing which rules to use. |
32 | Previous Block Hash | Double SHA-256 hash of the last block header, linking blocks together. |
32 | Merkle Root Hash | Double SHA-256 hash of all block transactions, checking they are correct. |
4 | Time | Unix time when hashing started. |
4 | nBits (Difficulty) | Target number the hash must be under. |
4 | Nonce | Number miners change to get new hashes. |
The miner uses SHA-256 to hash the block header. The goal is to get a hash under the network’s target. If the hash is too high, the miner changes the nonce and tries again. This happens millions of times each second on the network.
The whole network finds a good block about every 10 minutes. This timing stays steady because the mining difficulty changes every 2016 blocks, or about every two weeks.
Double SHA-256 Hashing
Bitcoin uses double SHA-256 hashing to stay safe. Miners run SHA-256 two times on the block header. This helps stop some attacks, like length extension attacks. Double hashing comes from cryptography research that showed it adds more safety.
Double SHA-256 hashing gives extra protection by hashing the hash again.
This does not stop collision attacks, but it makes length extension attacks harder.
Mining depends on SHA-256’s strength, so attacks are not possible with today’s tech.
SHA-256 works well with 32-bit CPUs and fits Bitcoin’s ECDSA-SHA-256 signatures.
The miner changes the nonce in the block header and uses double SHA-256 hashing. If the hash is under the target, the miner sends the block to the network. This keeps the blockchain safe and correct.
Nonce and Target Difficulty
The nonce is a 4-byte part of the block header. Miners use the nonce to make new hash results. Each time the nonce changes, SHA-256 makes a new hash. The goal is to find a hash lower than the target.
The nonce lets miners try many blocks fast.
Each try is different because SHA-256 is random.
If all nonce values fail, miners change other fields, like the time or extraNonce, to keep going.
Mining difficulty sets the limit for a good hash. The network changes this every 2016 blocks to keep block times near 10 minutes. If more miners join or get better machines, the hash rate goes up. The network then raises the difficulty, making mining harder. If miners leave, the difficulty drops, keeping things fair.
Bitcoin’s proof-of-work system uses this process. Mining keeps the network safe by making it hard and costly to change the blockchain. The nonce, target difficulty, and SHA-256 are the main parts of bitcoin mining.
Proof-of-work makes sure only miners who do real work can add blocks. This keeps the blockchain safe and spread out.
Bitcoin Mining Hardware
Evolution: CPU, GPU, ASIC
Bitcoin mining hardware has changed a lot since 2009. At first, people mined bitcoin with normal computers using CPUs. These computers were slow, but the network was small.
So, CPUs could still run the sha-256 algorithm. As more people started mining, it got harder to earn rewards. Miners switched to GPUs, which could do sha-256 much faster. Home miners built rigs with GPUs and joined mining pools. Later, FPGAs came out. They used less power and gave more control. But FPGAs were tricky to use and did not last long.
The biggest change happened with asic mining hardware. ASIC means application-specific integrated circuit. These chips are made for one thing: running sha-256 for bitcoin mining.
Consequently, cheaper options like CPUs and GPUs became obsolete for serious mining. ASICs now dominate the network, and their relentless advancement is clearly reflected in Bitcoin’s soaring global hash rate (over 1 ZettaHash/sec in 2025). ASIC miners quickly became the best choice for serious miners.
The table below shows how mining hardware changed over time:
Era | Years | Hardware Type | Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
2009-2010 | CPU | Mining started with CPUs; low hash rates; easy for early adopters | |
GPU Mining | 2010-2011 | GPU | GPUs outperformed CPUs; hash rate and cost efficiency improved; mining pools grew |
FPGA Mining | 2011-2012 | FPGA | Customizable hardware; better power efficiency; short adoption period |
ASIC Mining | 2013-present | ASIC | Designed for bitcoin mining; unmatched hash rates and energy efficiency; industrial scale mining |
What Are ASIC Miners?
ASIC miners are special bitcoin mining machines made for sha-256. The full name is application-specific integrated circuit. These machines use all their power for sha-256 math. ASIC miners can do double sha-256 hashing very fast. Each chip tries many nonces to find a hash under the target. ASIC mining hardware uses fans and heat sinks to keep cool. Since they only do one job, asic miners are much faster than CPUs or GPUs.
ASIC miners have smart designs. They pipeline and unroll sha-256 steps, so each chip makes a new hash every clock cycle. This gives them lots of hashing power and a better hash rate than old hardware. ASIC mining hardware also skips extra steps that are not needed, making things even faster.
How ASICs Optimize SHA-256 Calculation
ASIC mining hardware is faster and uses less power than CPUs or GPUs. ASICs can reach terahash per second speeds. GPUs only get hundreds of megahashes per second. ASICs use less power for each hash, so they are cheaper to run.
The table below compares the main types of bitcoin mining hardware:
Hardware Type | Specialization | Hash Rate | Energy Efficiency | Flexibility | Cost | Longevity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ASIC Miner | Highly specialized for sha-256 | Terahashes per second (TH/s) | Very high (low power per hash) | Low | High | Short |
GPU | General-purpose with parallelism | Megahashes per second (MH/s) | Moderate | High | Moderate | Longer |
CPU | General-purpose, complex cores | Low | Low | High |
ASIC mining hardware uses tricks to work better. They use pipelining, loop unrolling, and fast adders to speed up sha-256. Bitcoin mining does not need perfect accuracy, so asic miners balance speed and fault tolerance. This makes asic mining hardware the best for people who want more profit and a strong hash rate.
ASIC mining hardware is now the only way to win at bitcoin mining. The network keeps getting harder, so only asic miners with high power can keep up.
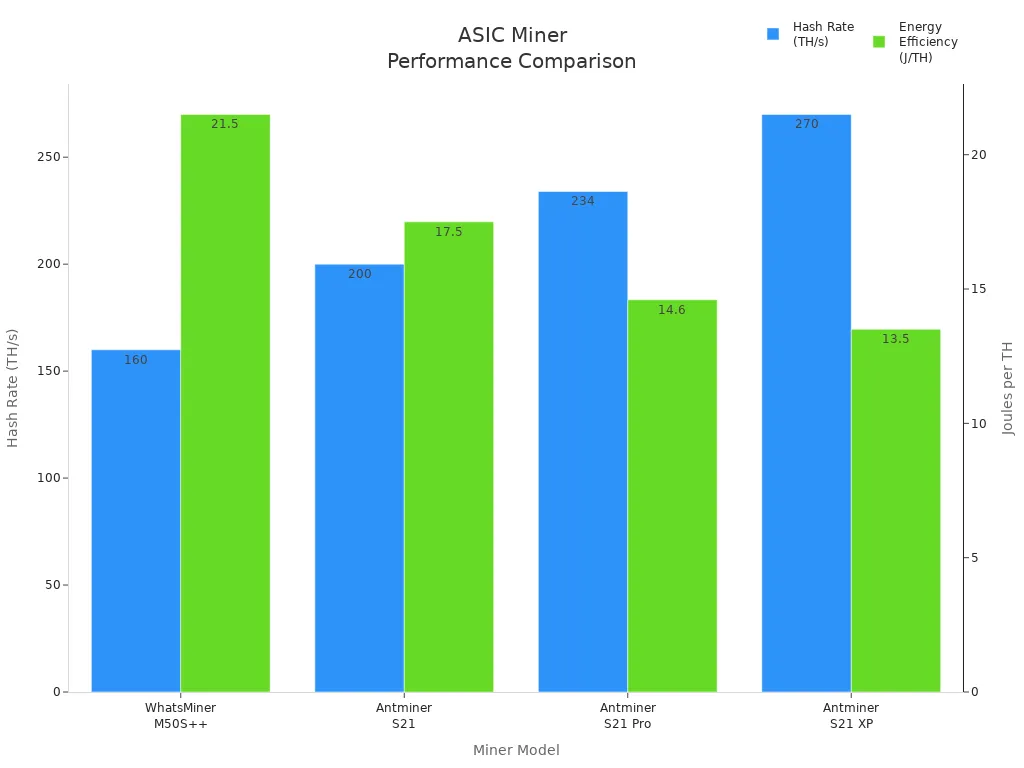
ASIC mining hardware keeps getting better. New models use less energy, have lower joules per terahash, and new cooling. The newest asic mining hardware can go over 200 TH/s and use as little as 13.5 J/TH. This shows asic mining hardware will stay important for bitcoin mining for a long time.
Top SHA-256 Coins and Mining Hardware
Leading SHA-256 Cryptocurrencies
Many digital coins use SHA-256 for mining. Bitcoin is the most famous one. But there are other coins that use sha-256 too. These coins have similar safety because they use the same algorithm. Some coins, like Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin SV, split from bitcoin. They kept the same mining way. Others, like Digibyte and Peercoin, picked SHA-256 for its strong safety.

Many coins that use sha-256 can use the same bitcoin mining hardware. This makes it simple for miners to move to other networks if they want.
Bitcoin has the biggest market and network. Other coins, like Namecoin, use SHA-256 too. But their networks are much smaller. Using the same algorithm lets miners use their hardware for many coins.
Top-Performing SHA-256 Miners
Bitcoin mining hardware has undergone major changes, with ASIC miners now being the preferred option because they’re faster and more energy-efficient. Miners want hardware that does more hashes per second and uses less power.
The table below lists some of the best models:
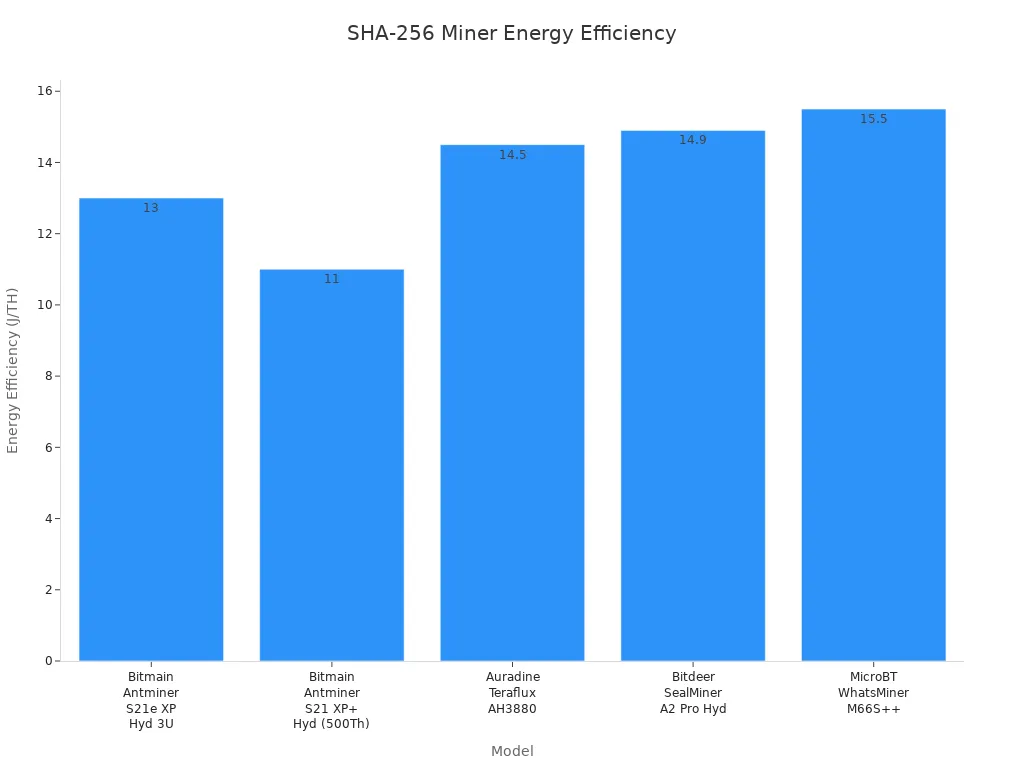
Mining pools use bitcoin mining hardware to get more rewards. They break mining into small jobs called shares. Each miner uses asic hardware to solve these jobs. The pool keeps track of each miner’s work. It gives rewards based on how much work each miner does. This helps miners get steady payouts instead of mining alone.
Tip: Picking the right bitcoin mining hardware is important for making money. Miners should check hash rate, energy use, and cooling before buying new machines.
SHA-256 and ASICs help keep Bitcoin safe and strong. Miners used CPUs first, but now they use ASICs. This change made hash rates go up. The network is safer because of this.
New ASICs use less power and help miners earn money.
The network changes difficulty every two weeks to stay safe.
Higher hash rates make it harder for bad people to attack.
Trend | Details |
|---|---|
Energy Efficiency | ASICs now use only 21 joules for each TH |
Hardware Evolution | Miners switched from CPUs to ASICs in 2016 |
Security | More hash rate means better network safety |
If you want to learn about blockchain or mining, knowing these changes helps. It shows how Bitcoin stays safe and why mining keeps changing.


























 Avalon
Avalon Bitdeer
Bitdeer Bitmain
Bitmain BOMBAX
BOMBAX DragonBall
DragonBall Elphapex
Elphapex Fluminer
Fluminer Goldshell
Goldshell iBelink
iBelink Iceriver
Iceriver Ipollo
Ipollo Jasminer
Jasminer Volcminer
Volcminer Aleo Miner
Aleo Miner Dash Miner
Dash Miner Doge<C Miner
Doge<C Miner Grin Miner
Grin Miner Handshake(HNS) Miner
Handshake(HNS) Miner Kadena(KDA) Miner
Kadena(KDA) Miner Monero(XMR) Miner
Monero(XMR) Miner Nexa Miner
Nexa Miner Ravencoin(RXD) Miners
Ravencoin(RXD) Miners ScPrime(SCP) Miner
ScPrime(SCP) Miner